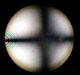
Conoscopy |
| This page presents some examples of convergent light figures (conoscopic images) obtained with the petrographic microscope. The pictures were photographed with a phase contrast telescope inserted between the photo tube of the microscope and a bellow accessory attached to a digital camera. The phase contrast telescope has the same function as a Bertrand lens but it is generally much less expensive. In the first two group of pages, a non mathematical explanation of the features that can be observed in the conoscopic figures is developed with the help of diagrams and pictures.
|
|
Conoscopy of Uniaxial Minerals. Illustration and practical explanations of images structures. ( February 2004). 2. Images in monochromatic light. 4. Use of quarter wave, Benford plate and quartz Wedge. 5. Conoscopy of crystals cut parallel to optic axis.
|
|
 |
Conoscopy of biaxial minerals. ( February - March 2004 ) 2. Figures perpendicular to the acute bisectrix. 3. Figures normal to one optic axis. 4. Accessory plates: 1l and 1/4 l plates.
|
| Animation of a conoscopic picture of a muscovite crystal cut along the cleavage plan ( perpendicular to the acute bisectrix). Click for movie. Observe that isogyres are counter rotating around the poles of the optic axes.
|
|
 |
Beryl (Aqua Marine) normal to the optic axis. Beryl is sometimes pseudo biaxial. |
 |
Biotite, pseudo uniaxial. |
 |
Images of quartz nearly perpendicular to the optical axis
|
|
Topaz plate cut nearly perpendicular to acute bisectrix. |
|
|
Random section of gypsum. |
|
 |
Feldpath nearly perpendicular to one optical axis.
|
 |
Optic dispersion in chloritoid. |